Flagellum means whip in Latin. It is a whip-like appendage found on cell surfaces of archaea, bacteria and protozoans. Flagella in these cells are used mainly for locomotion. However, flagella (plural) is not to be confused with pili
Types of flagella
- Bacterial flagella
- Archaea flagella
- Protozoan flagella
Bacterial Flagella
Flagellated bacteria are classified into four based on the position of the flagella on their cell wall into the following:
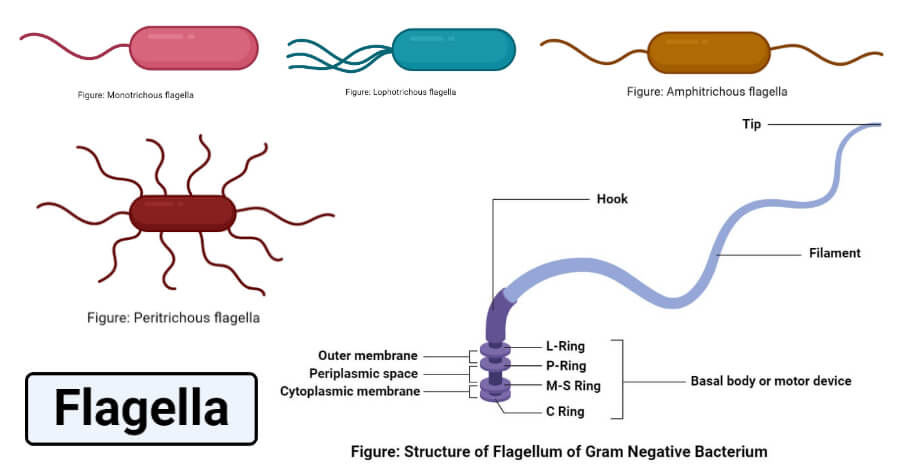
- Monotrichous bacteria: These are bacteria that possess only one flagellum at one end of their cell wall. An example is Vibrio cholera, the causal agent of cholera.
- Lophotrichous bacteria: These are bacteria that have multiple flagella that protrude from a single portion of their cell wall. An example is
- Amphitrichous bacteria: These are bacteria that have a flagellum each at opposite ends on their cell surface. In amphitrichous bacteria, the two flagella cannot be active at a time. When one of the flagella is active, the other will be dormant and vice versa. Moreover, the presence of flagellum at opposite ends allows the bacteria possessing such to change course swiftly during movement. An example is Alcaligenes faecalis
- Peritrichous bacteria: These are bacteria that have flagella protruding from all part of their cell surface. An example is Escherichia coli.
Archaea Flagella
Archaeal flagella is similar in all respect to bacterial flagella, it is also made up of protein sub-unit called flagellin except that it has a type-iv pilus-like structure.
Protozoan Flagella
- Flagellated protozoans include organisms classified under sub-phylum Mastigophora; they include the zooflagellates such as Trichomonas vaginalis and Trypanosoma gambienses and phytoflagellates such as Euglena and Volvox species which are taxonomically under the class Zoomastigophora and Phytomastigophora respectively. The zooflagellates are the plant-like protozoans while the phytoflagellates are the plant like protozoans. See – the five kingdoms in biology
Composition and structure
The flagellum is made up of three distinct parts: filament, hook and basal body. The filament is the whip-like part of the flagella, while the hook as the name implies attach the filament to the basal body of the microorganism. The basal body is the body of the archaea, bacteria or protozoan where the filament protrudes. The major difference between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms is that; prokaryotic cells flagella are made up of protein sub-unit called flagellin while protozoan flagella are made up of proteins called microtubules
Function
Flagellum is used mainly for locomotion in prokaryotes as well as sensation, signal transduction, adhesion. It is also said to be a virulence factor. For instance, Helicobacter pylori, the causal agent of gastric ulcer moves toward the intestinal lining of human where it causes damage to the epithelium with the aid of its flagella.
